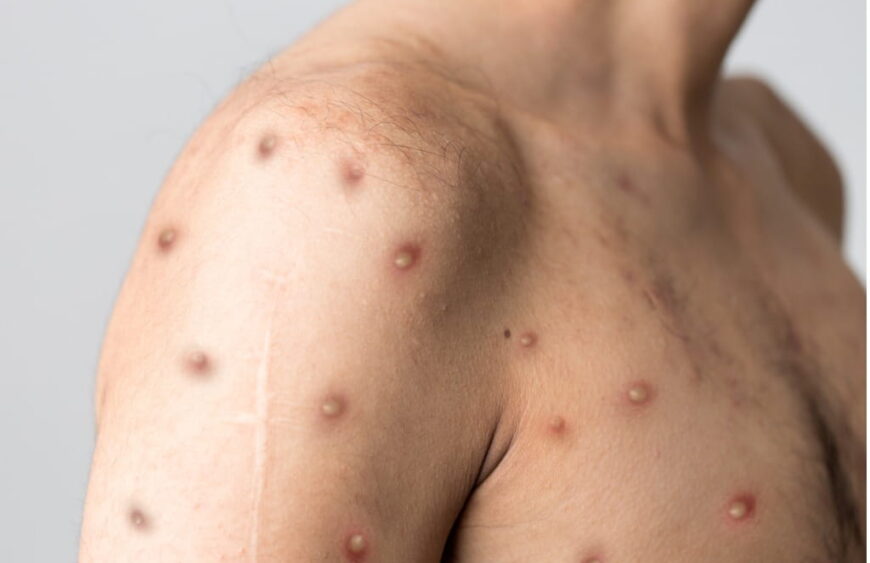
Introduction
Monkeypox, a viral zoonotic disease, has recently gained attention due to outbreaks in several parts of the world. While it shares similarities with smallpox, monkeypox is generally less severe but still poses a significant public health concern. Rapid and accurate detection is crucial for controlling the spread of the virus, and one of the most effective tools in this effort is the Monkeypox RT-PCR Detection Kit. In this blog, we’ll explore what monkeypox is, how it spreads, and the importance of RT-PCR testing in diagnosing this emerging infectious disease.
What is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is caused by the Monkeypox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes the viruses that cause smallpox and cowpox. The disease was first identified in laboratory monkeys in 1958, but it primarily affects rodents and other wild animals. Human cases of monkeypox were first reported in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 1970, and since then, the virus has been detected in various parts of Africa, and more recently, in other regions across the globe.
Monkeypox presents with symptoms similar to those of smallpox, including fever, headache, muscle aches, and a characteristic rash that progresses to pustules and scabs. However, monkeypox is generally less contagious and less deadly than smallpox. The incubation period for monkeypox ranges from 5 to 21 days, and the illness typically lasts for 2 to 4 weeks.
Transmission of Monkeypox
Monkeypox can spread from animals to humans through direct contact with the blood, bodily fluids, or skin lesions of infected animals. Human-to-human transmission occurs through respiratory droplets, direct contact with an infected person’s lesions, or indirect contact via contaminated materials such as bedding or clothing.
Given its mode of transmission, monkeypox can spread quickly in close-contact settings, such as households, healthcare facilities, and crowded environments. Early detection and isolation of infected individuals are critical in preventing widespread outbreaks.
The Importance of RT-PCR in Monkeypox Detection
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) is a powerful molecular technique used to detect the presence of specific genetic material from a pathogen, such as the Monkeypox virus. RT-PCR has become the gold standard for diagnosing various viral infections, including monkeypox, due to its high sensitivity, specificity, and speed.
The Monkeypox RT-PCR Detection Kit is designed to identify the genetic material of the Monkeypox virus in clinical samples, such as swabs from skin lesions, blood, or respiratory specimens. This kit works by amplifying the viral DNA, allowing for the detection of even small amounts of the virus in the sample.
Key Benefits of Using the Monkeypox RT-PCR Detection Kit:
- Rapid Results: The RT-PCR process can deliver results within hours, enabling healthcare providers to make quick and informed decisions about patient care and public health responses.
- High Sensitivity and Specificity: The kit is designed to specifically target the genetic sequences of the Monkeypox virus, minimizing the chances of false positives or negatives.
- Early Detection: RT-PCR can detect the virus even in the early stages of infection, allowing for timely intervention and reducing the risk of further transmission.
- Scalability: The RT-PCR Detection Kit can be used in various laboratory settings, from small clinics to large reference labs, making it an accessible tool for widespread testing.
How the Monkeypox RT-PCR Detection Kit Works
The process of using the Monkeypox RT-PCR Detection Kit involves several key steps:
- Sample Collection: Clinical samples, such as swabs from skin lesions or respiratory specimens, are collected from the patient.
- RNA Extraction: The viral RNA is extracted from the sample using specialized reagents. This step is crucial for ensuring that the genetic material is purified and ready for amplification.
- RT-PCR Amplification: The extracted RNA is then subjected to the RT-PCR process, where it is converted into complementary DNA (cDNA) and amplified using specific primers that target the Monkeypox virus’s genetic sequences.
- Detection: The amplified DNA is detected using fluorescent markers, which indicate the presence of the Monkeypox virus in the sample. The results are typically displayed in real-time, allowing for immediate interpretation.
- Result Interpretation: The final step involves analyzing the data to determine whether the Monkeypox virus is present in the sample. A positive result indicates an active infection, while a negative result suggests the absence of the virus.
The Role of RT-PCR in Controlling Monkeypox Outbreaks
RT-PCR testing plays a crucial role in managing monkeypox outbreaks by enabling early detection and rapid response. By identifying infected individuals quickly, public health officials can implement control measures such as isolation, contact tracing, and vaccination (where available) to prevent further spread.
Additionally, the ability to accurately diagnose monkeypox helps differentiate it from other diseases with similar symptoms, such as chickenpox or smallpox, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care and treatment.
Conclusion
As monkeypox continues to emerge as a global health concern, the need for reliable and efficient diagnostic tools becomes increasingly important. The Monkeypox RT-PCR Detection Kit stands out as a vital resource in the fight against this virus, offering rapid, accurate, and early detection that is essential for controlling outbreaks and protecting public health.
By leveraging advanced molecular techniques like RT-PCR, healthcare providers and public health officials can stay ahead of the curve, ensuring that monkeypox is detected and contained before it can cause widespread harm.