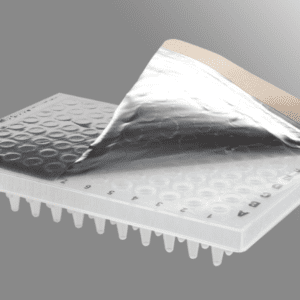
Axygen® 60 µm CyclerSeal Sealing Film for Storage and PCR Application, Nonsterile
Original price was: د.إ 1,030.43.د.إ 666.00Current price is: د.إ 666.00.
In stock, 20 units
Axygen® microplate sealing films are designed for applications ranging from PCR and Real-Time PCR to ELISA and cell culture. Axygen’s sealing films are the easiest…
Axygen® 70µm Ultra Clear Pressure Sensitive Sealing Film for Real Time PCR, Nonsterile
د.إ 1,831.79
In stock, 4 units
Axygen® 70µm Ultra Clear Pressure Sensitive Sealing Film is a high-quality laboratory consumable used for sealing microplates during real-time PCR experiments. The film is designed…
Axygen® PCR 35 µm Aluminum Sealing Film For Thermal Sealing and General Sealing Purposes, Nonsterile
د.إ 2,552.15
Axygen® microplate sealing films are designed for applications ranging from PCR and Real-Time PCR to ELISA and cell culture. Axygen’s sealing films are the easiest…
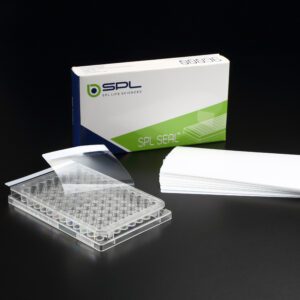
SPL SEAL™, PET/acrylate, Clear, 141x79mm(PCR Plate Films and Seals)
د.إ 485.03
In stock, 2 units
Download SPL Life Sciences 2023 Products Catalogue .pdf
…