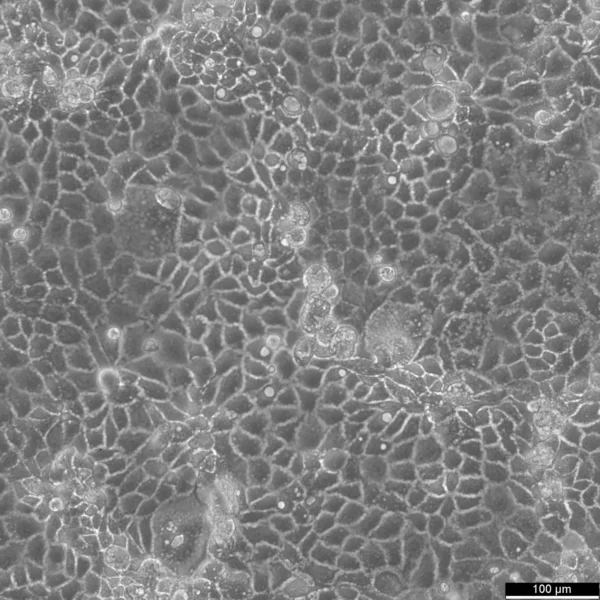
Caco-2 Cells
Description
Caco-2 Cells
Caco-2 cells serve as an advanced in vitro model for the human intestinal barrier, primarily due to their differentiation into a cell monolayer that closely resembles the enterocytes lining the small intestine. When culturing the Caco2 cell line on tissue culture filter inserts with polycarbonate filters, Caco-2 cells undergo spontaneous differentiation. The differentiation of Caco2 cells results in the expression of specialized cell types, complete with microvilli, enzymes, and transporters, paralleling the complex features and mechanisms found in an in vivo situation.
In the context of intestinal absorption studies models, Caco-2 cells, which were derived from a human colorectal adenocarcinoma patient, are instrumental due to their ability to develop high TEER values, signifying intact tight junctions and epithelial barrier function. These properties are crucial for assays like the cholesterol efflux assay and investigations into cellular transport, including the movement of lipid nanoparticles and the detection of protein interactions.
Caco-2 cells are pivotal for intestinal absorption studies, providing a reliable in vitro approximation of the intestinal epithelium. Mimicking intestinal enterocytes, these cells facilitate analyses of oral drug absorption by simulating the intestinal barrier. Researchers utilize Caco-2 cells to predict how substances traverse the intestinal mucosa, which is essential for the pharmacokinetic profiling of oral medications. Furthermore, they are a key tool in investigating intestinal cholesterol uptake, homeostasis and transport, which are vital processes for understanding lipid metabolism and associated diseases.
Caco-2 cells remain a cornerstone in colon carcinoma and toxicology research, not only for their relevance to human gastrointestinal studies but also for their role in providing detailed insights into the biliary pathway, the metabolism of xenobiotics within the colon, cancer and toxicology research.
| Organism | Human |
|---|---|
| Tissue | Colon |
| Disease | Adenocarcinoma |
| Applications | Model of the GI (gastrointestinal) tract, measurement of the Trans-Epithelial/Endothelial Eletrical Resistance (TEER). Caco-2 cells develop high TEER values of up to 2000 cm2 (as measured by CLS using the CellZscope, nanoAnalytics, M?nster, Germany). |
| Synonyms | CaCo-2, CACO-2, Caco 2, CACO 2, CACO2, CaCo2, CaCO2, Caco2, Caco-II |
| Age | 72 years |
|---|---|
| Gender | Male |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian |
| Morphology | Epithelial-like |
| Growth properties | Adherent |
Cytion
There are no question found.








Rating & Review
There are no reviews yet.